⚠️ This blog post was created with the help of AI tools. Yes, I used a bit of magic from language models to organize my thoughts and automate the boring parts, but the geeky fun and the 🤖 in C# are 100% mine.
Hi!
In my previous post, I showed you how to orchestrate multiple AI agents using the Microsoft Agent Framework, connecting Azure AI Foundry (OpenAI), GitHub Models, and Ollama in a single .NET 9 application. Today, I’m taking this a step further by introducing Azure AI Foundry Persistent Agents—a powerful feature that allows you to create, manage, and track agents directly in the Azure AI Foundry portal.
This enhanced demo showcases a three-agent workflow that not only orchestrates models across different providers but also leverages Azure AI Foundry’s persistent agent capabilities for better lifecycle management, observability, and collaboration.
Note: If you want to avoid the full blog post, just go to lesson 6 here >> https://aka.ms/genainet
🎯 What’s new in this demo
Building on the original multi-model orchestration concept, this version introduces:
| Agent | Provider | Model | Special Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🧠 Researcher | Azure AI Foundry Persistent Agent | gpt-4o-mini | Created and managed in Azure AI Foundry portal |
| ✍️ Writer | Azure OpenAI or GitHub Models | gpt-4o-mini | Flexible authentication (API key, managed identity, or GitHub token) |
| 🔍 Reviewer | Ollama (local) | llama3.2 | Privacy-focused local inference |
The key difference? The Researcher agent is now a persistent agent that lives in Azure AI Foundry. This means you can:
- ✅ View and manage agents directly in the Azure portal
- ✅ Track agent execution through conversation threads
- ✅ Monitor agent performance and behavior over time
- ✅ Share agents across team members and applications
- ✅ Clean up agents programmatically or through the portal
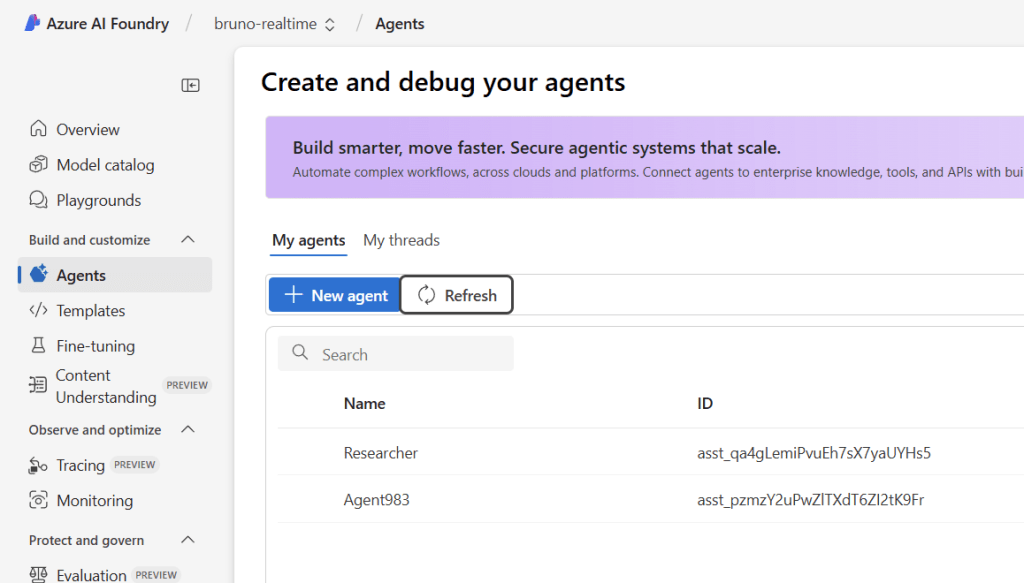
🏗️ Architecture: Persistent Agents + Multi-Provider Workflow
The workflow remains sequential, but now with enhanced cloud-native agent management:
User Input
↓
Azure AI Foundry Persistent Agent (Researcher)
↓ (research findings)
Azure OpenAI/GitHub Models Agent (Writer)
↓ (article draft)
Ollama Local Agent (Reviewer)
↓
Final Output (reviewed article with feedback)
Each agent reports telemetry to OpenTelemetry, giving you complete visibility across the entire pipeline—from cloud to local models.
🧠 Understanding Azure AI Foundry Persistent Agents
What makes persistent agents special?
Traditional agents are ephemeral—they exist only during your application’s runtime. Persistent agents, on the other hand, are first-class resources in Azure AI Foundry:
- Cloud-Native Management: Agents are created via the Azure AI Foundry SDK and appear in the portal immediately
- Thread-Based Conversations: Each agent execution creates a conversation thread that’s stored and viewable
- Lifecycle Control: Create, update, delete, and monitor agents through both code and UI
- Team Collaboration: Share agents across projects and team members within your AI Foundry workspace
- Audit & Compliance: Track agent usage, performance, and history for governance purposes
The AIFoundryAgentsProvider abstraction
To simplify working with persistent agents, I created the AIFoundryAgentsProvider class:
public static AIAgent CreateAIAgent(string name, string instructions)
{
var persistentAgentsClient = CreatePersistentAgentsClient();
AIAgent aiAgent = persistentAgentsClient.CreateAIAgent(
model: _config.DeploymentName,
name: name,
instructions: instructions);
return aiAgent;
}
private static PersistentAgentsClient CreatePersistentAgentsClient()
{
return new PersistentAgentsClient(
_config.AzureFoundryProjectEndpoint!,
new AzureCliCredential());
}
This abstraction:
- Uses
AzureCliCredentialfor secure, credential-free authentication - Creates agents directly in your Azure AI Foundry project
- Returns an
AIAgentthat works seamlessly with the Microsoft Agent Framework - Provides cleanup methods to delete agents when you’re done
🔐 Authentication: Secure by default
The persistent agent uses Azure CLI credentials (AzureCliCredential), which means:
✅ No API keys in code or config
✅ Works with az login for local development
✅ Production-ready with managed identities
✅ Follows Azure security best practices
For the Writer agent, the demo supports three authentication options with automatic fallback:
🥇 Option 1: GitHub Models (Fastest for prototyping)
dotnet user-secrets set "GITHUB_TOKEN" "your-github-token"
dotnet user-secrets set "deploymentName" "gpt-4o-mini"
🥈 Option 2: Azure OpenAI with API Key
dotnet user-secrets set "endpoint" "https://your-resource.cognitiveservices.azure.com"
dotnet user-secrets set "apikey" "your-azure-openai-api-key"
dotnet user-secrets set "deploymentName" "gpt-4o-mini"
🥉 Option 3: Azure OpenAI with Managed Identity (Most secure)
dotnet user-secrets set "endpoint" "https://your-resource.cognitiveservices.azure.com"
dotnet user-secrets set "deploymentName" "gpt-4o-mini"
az login # Required for local development
The ChatClientProvider automatically selects the best available option:
public static IChatClient GetChatClient()
{
if (_config.HasValidGitHubToken)
{
return CreateGitHubModelsClient();
}
return CreateAzureOpenAIClient();
}
🧩 The complete workflow in action
Let’s walk through a real execution of the demo with OpenTelemetry traces showing each agent’s performance:
Step 1: Agent Setup
=== Microsoft Agent Framework - Multi-Model Orchestration Demo ===
This demo showcases 3 agents working together:
1. Researcher (Azure AI Foundry Agent) - Researches topics
2. Writer (Azure OpenAI or GitHub Models) - Writes content based on research
3. Reviewer (Ollama - llama3.2) - Reviews and provides feedback
Setting up Agent 1: Researcher (Azure AI Foundry Agent)...
Setting up Agent 2: Writer (Azure OpenAI or GitHub Models)...
Setting up Agent 3: Reviewer (Ollama)...
Creating workflow: Researcher -> Writer -> Reviewer
Starting workflow with topic: 'artificial intelligence in healthcare'
Step 2: Researcher Agent Execution (Azure AI Foundry)
The persistent Researcher agent springs into action, creating a conversation thread in Azure AI Foundry:
Activity.DisplayName: invoke_agent Researcher
Activity.Kind: Client
Activity.StartTime: 2025-10-16T15:51:56.1426555Z
Activity.Duration: 00:00:40.0433429
Activity.Tags:
gen_ai.operation.name: chat
gen_ai.usage.output_tokens: 2113
⏱️ Duration: 40 seconds
📊 Output tokens: 2,113 tokens of comprehensive research
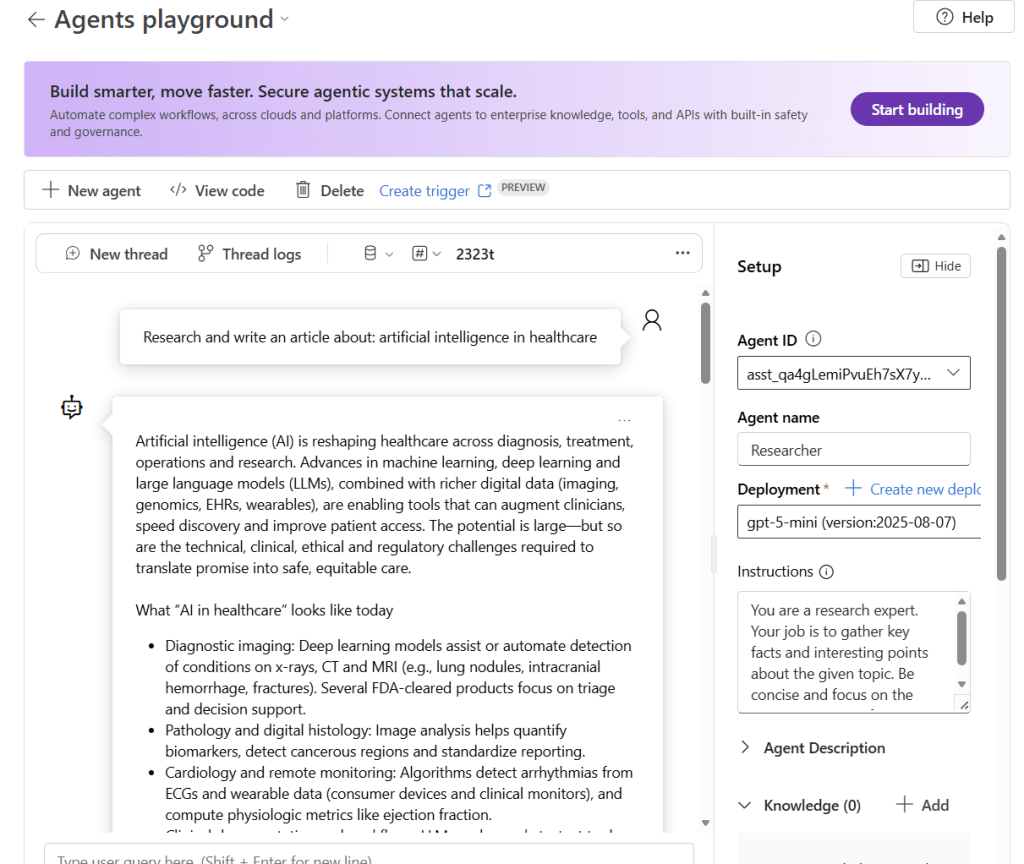
Step 3: Writer Agent Execution (Azure OpenAI/GitHub Models)
The Writer takes the research and crafts an engaging article:
Activity.DisplayName: invoke_agent Writer
Activity.Kind: Client
Activity.StartTime: 2025-10-16T15:52:36.2113339Z
Activity.Duration: 00:00:31.4054205
Activity.Tags:
gen_ai.operation.name: chat
gen_ai.usage.output_tokens: 1629
⏱️ Duration: 31 seconds
📊 Output tokens: 1,629 tokens of polished content
Step 4: Reviewer Agent Execution (Ollama Local)
Finally, the local Ollama model provides feedback:
Activity.DisplayName: invoke_agent Reviewer
Activity.Kind: Client
Activity.StartTime: 2025-10-16T15:53:07.6191258Z
Activity.Duration: 00:00:07.4031237
Activity.Tags:
gen_ai.operation.name: chat
gen_ai.usage.output_tokens: 531
⏱️ Duration: 7.4 seconds
📊 Output tokens: 531 tokens of constructive feedback
Notice how the local Ollama model is significantly faster (7.4s vs 31-40s) because it runs on your machine without network latency. This demonstrates the power of hybrid architectures—using cloud models for complex tasks and local models for faster, privacy-sensitive operations.
📊 The final output: AI-powered content creation pipeline
After all three agents complete their work, you get a comprehensive article about AI in healthcare:
=== Final Output ===
Title: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare - Key Facts, Applications,
Opportunities, and Risks
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) applies algorithms and statistical models to
perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. In healthcare, AI
ranges from rule-based decision support to deep learning and large language
models (LLMs). It's being used to augment clinical care, accelerate research,
automate administrative tasks, and expand access to services...
[Full article content with research, engaging writing, and editorial feedback]
**Overall Assessment**
The article provides an in-depth analysis of artificial intelligence (AI)
in healthcare, covering its applications, benefits, challenges, and regulatory
landscape. The text is well-structured, with clear sections on different topics
and concise explanations...
**Recommendations for Improvement**
1. Simplify technical language: Use clear, concise definitions...
2. Improve transitions and connections: Add transitional phrases...
3. Balance benefits and challenges: Include more nuanced discussions...
The result is a production-ready article that went through research, creative writing, and editorial review—all automated through agent orchestration.
🧹 Agent lifecycle management
One of the most powerful features of persistent agents is lifecycle control. At the end of execution, the demo prompts:
=== Clean Up ===
Do you want to delete the Researcher agent in Azure AI Foundry? (yes/no)
yes
Deleting Researcher agent in Azure AI Foundry...
Researcher agent deleted successfully.
This cleanup is done programmatically:
public static void DeleteAIAgentInAIFoundry(AIAgent agent)
{
var persistentAgentsClient = CreatePersistentAgentsClient();
persistentAgentsClient.Administration.DeleteAgent(agent.Id);
}
You can also manage agents directly in the Azure portal:
- ✅ View all agents in your project
- ✅ Inspect conversation threads and execution history
- ✅ Delete or update agents through the UI
- ✅ Share agents with team members
This gives you operational flexibility—manage agents as code during development, then transition to UI-based management for production monitoring.
💡 Key takeaways and best practices
✅ When to use persistent agents
Use persistent agents when you need:
- Long-running agents that persist across application restarts
- Team collaboration on shared agents
- Audit trails and conversation history
- Portal-based monitoring and management
- Enterprise governance and compliance
Use ephemeral agents (ChatClientAgent) when:
- Building quick prototypes
- Creating short-lived, task-specific agents
- Running entirely local workflows
- Avoiding cloud dependencies
✅ Multi-provider benefits
This hybrid approach gives you:
- Best tool for the job: Use cloud models for complex reasoning, local models for speed
- Cost optimization: Reserve expensive cloud calls for tasks that need them
- Privacy control: Keep sensitive data local with Ollama
- Resilience: Failover between providers if one is unavailable
- Flexibility: Swap providers without changing your application logic
✅ OpenTelemetry observability
The built-in tracing provides:
- Performance metrics for each agent
- Token usage for cost tracking
- End-to-end visibility across the workflow
- Debugging insights when agents misbehave
🛠️ Try it yourself
Prerequisites
- .NET 9 SDK or later
- Azure CLI installed and authenticated (
az login) - Azure AI Foundry Project with model deployments
- Ollama with
llama3.2model installed - GitHub Token or Azure OpenAI credentials (optional)
Quick start
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/Generative-AI-for-beginners-dotnet
cd Generative-AI-for-beginners-dotnet/06-AgentFx/src/AgentFx-MultiAgents
- Set up Ollama:
# Install from https://ollama.com
ollama pull llama3.2
ollama run llama3.2
- Configure secrets:
# Required: Azure AI Foundry
dotnet user-secrets set "AZURE_FOUNDRY_PROJECT_ENDPOINT" "https://your-project.services.ai.azure.com/"
dotnet user-secrets set "deploymentName" "gpt-5-mini"
# Optional: GitHub Models (recommended for quick start)
dotnet user-secrets set "GITHUB_TOKEN" "your-github-token"
# OR Optional: Azure OpenAI
dotnet user-secrets set "endpoint" "https://your-resource.cognitiveservices.azure.com"
dotnet user-secrets set "apikey" "your-azure-openai-api-key"
- Authenticate with Azure:
az login
- Run the demo:
dotnet run
📖 Full documentation
For complete setup instructions, troubleshooting, and customization options, check out the detailed README in the repository.
🚀 What’s next?
This demo opens up exciting possibilities:
- Multi-agent collaboration: Add more specialized agents (SEO optimizer, fact-checker, translator)
- Parallel workflows: Run agents concurrently instead of sequentially
- Tool integration: Connect agents to databases, APIs, and MCP servers
- Production deployment: Scale with Azure Container Apps or Azure Functions
- Custom models: Fine-tune models for domain-specific tasks
The Microsoft Agent Framework makes all of this possible with a clean, .NET-native API.
🔗 References
- 💻 Demo repo: AgentFx-MultiAgents
- 📘 Microsoft Agent Framework: Official Documentation
- 🏗️ Azure AI Foundry: Portal
- 🧠 Microsoft.Extensions.AI: NuGet Package
- 🦙 Ollama: Official Website
🎬 Conclusion
Azure AI Foundry Persistent Agents bring enterprise-grade agent management to .NET 9, making it easier than ever to build, monitor, and maintain multi-agent systems. Combined with the flexibility of multi-provider orchestration and the observability of OpenTelemetry, you have everything you need to create production-ready AI applications.
Whether you’re building content creation pipelines, customer support systems, or research automation tools, this pattern provides a solid foundation for scalable, observable, and maintainable AI agent architectures.
Happy coding!
Greetings
El Bruno
More posts in my blog ElBruno.com.
More info in https://beacons.ai/elbruno
Leave a comment